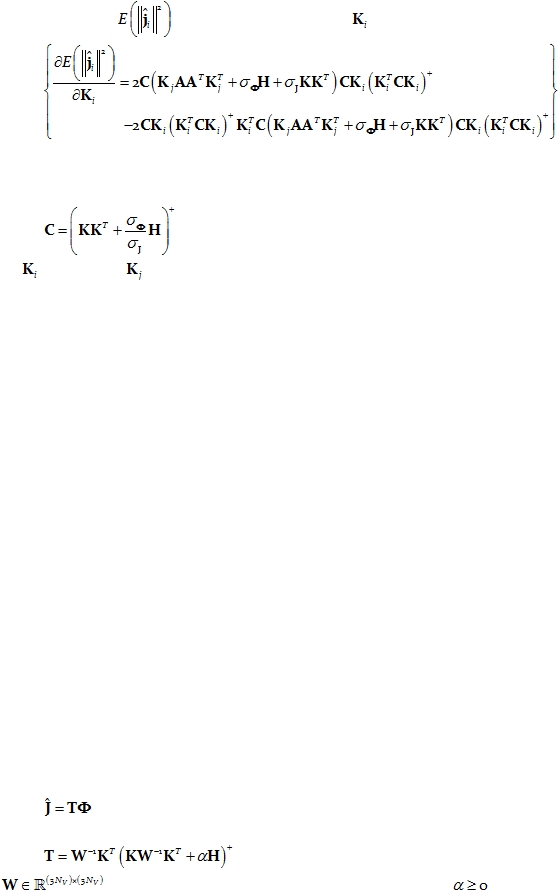
Cite as: “R.D. Pascual-Marqui: Discrete, 3D distributed, linear imaging methods of electric neuronal activity. Part 1: exact, zero
error localization. arXiv:0710.3341 [math-ph], 2007-October-17, http://arxiv.org/pdf/0710.3341 ”
Page 6 of 16
The derivative of
in Eq. 24 with respect to
is:
Eq. 25:
It can be easily shown
that the derivative in Eq. 25
is zero for the sLORETA case,
when the parameter matrix is:
Eq. 26:
and when
is equal to
, thus demonstrating that sLORETA produces exactly localized
maxima to point-test sources anywhere in the brain, even in the presence of noise, i.e.
sLORETA is unbiased.
This new result is to be contrasted with those published by Sekihara et al (2005) and
Greenblatt et al (2005). They showed that under pure measurement noise, sLORETA is
biased, and only attains exact localization under ideal conditions of no noise. They did not
consider the more realistic case where the brain in general is always active, as modeled here
by the biological noise. Under these arguably much more realistic conditions, sLORETA is
unbiased.
6.
eLORETA: exact low resolution brain electromagnetic tomography
The eLORETA method was developed and officially recorded as a working project at
the University of Zurich in March 2005. A description (including the official registration
date) can be obtained from the University of Zurich server at:
An additional reference to eLORETA is:
Roberto D. Pascual-Marqui, Alberto D. Pascual-Montano, Dietrich Lehmann, Kieko Kochi,
Michaela Esslen, Lutz Jancke, Peter Anderer, Bernd Saletu, Hideaki Tanaka, Koichi Hirata, E.
Roy John, Leslie Prichep. Exact low resolution brain electromagnetic tomography
(eLORETA). Neuroimage 2006, Vol 31, Suppl. 1, page:S86
Consider the general weighted minimum norm solution (see, e.g. Pascual-Marqui
1999):
Eq. 27:
with:
Eq. 28:
where
denotes the symmetric weight matrix, and
denotes the
regularization parameter.